doppler4arduino
Doppler - CortexM4 meets FPGA
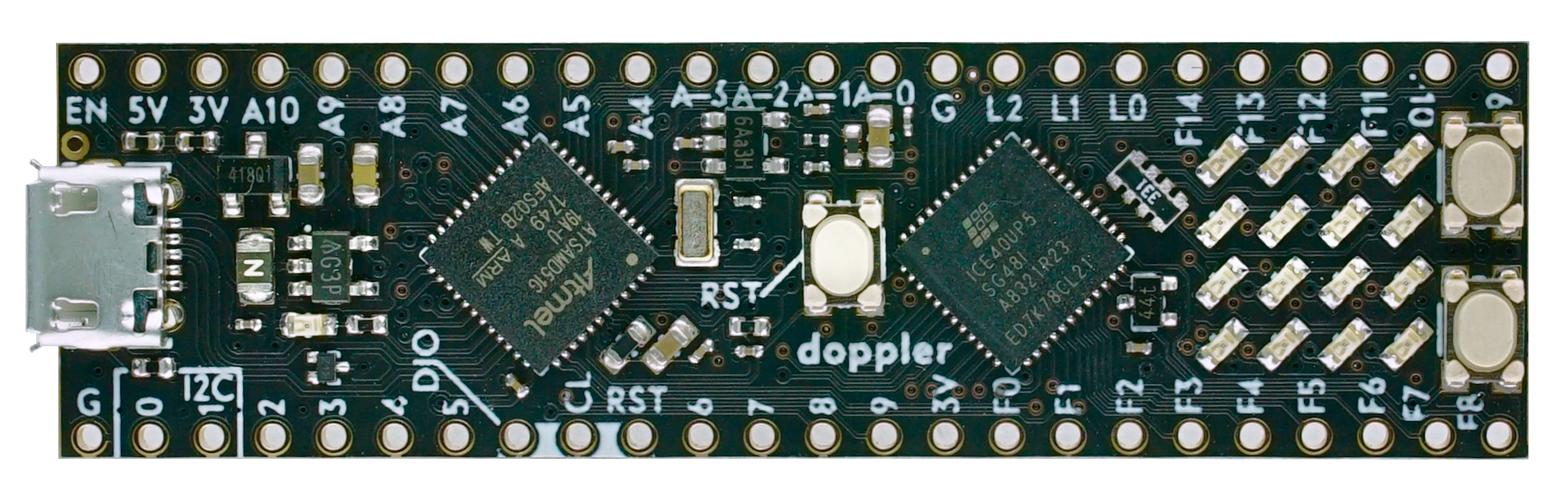
- arduino compatible board
- 120Mhz ARM Cortex M4 MCU 1MB Flash (samd51g19a) with FPU
- FPGA 5000 LUT, 1MBit RAM, 6 DSP Cores,OSC, PLL (Lattice ice40up5k)
- breadboard friendly (DIL48)
- micro usb
- power over USB or external via pin headers
- VCC 3.5V …. 5.5V
- all GPIO Pins are 3.3V
- 1 led connected to samd51
- 4 x 4 LED Matrix (connected on fpga)
- 2 Custom Buttons (connected on fpga)
- ARef Solder Jumper
- I2C (need external pullup), SPI, QSPI Pins
- 2 DAC pins, 10 ADC pins
- full opensource toolchain
- SWD programming pin headers
- double press reset to enter the bootloader
- uf2 bootloader with Firmwareupload via simple USB stick mode
Builds based on this repo: https://github.com/noscene/ArduinoCore-samd
Setup
First need install the arduino ide from
- https://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/Software
then add board URLs (comma separated):
- https://adafruit.github.io/arduino-board-index/package_adafruit_index.json,
- https://noscene.github.io/doppler4arduino/package_doppler_index.json
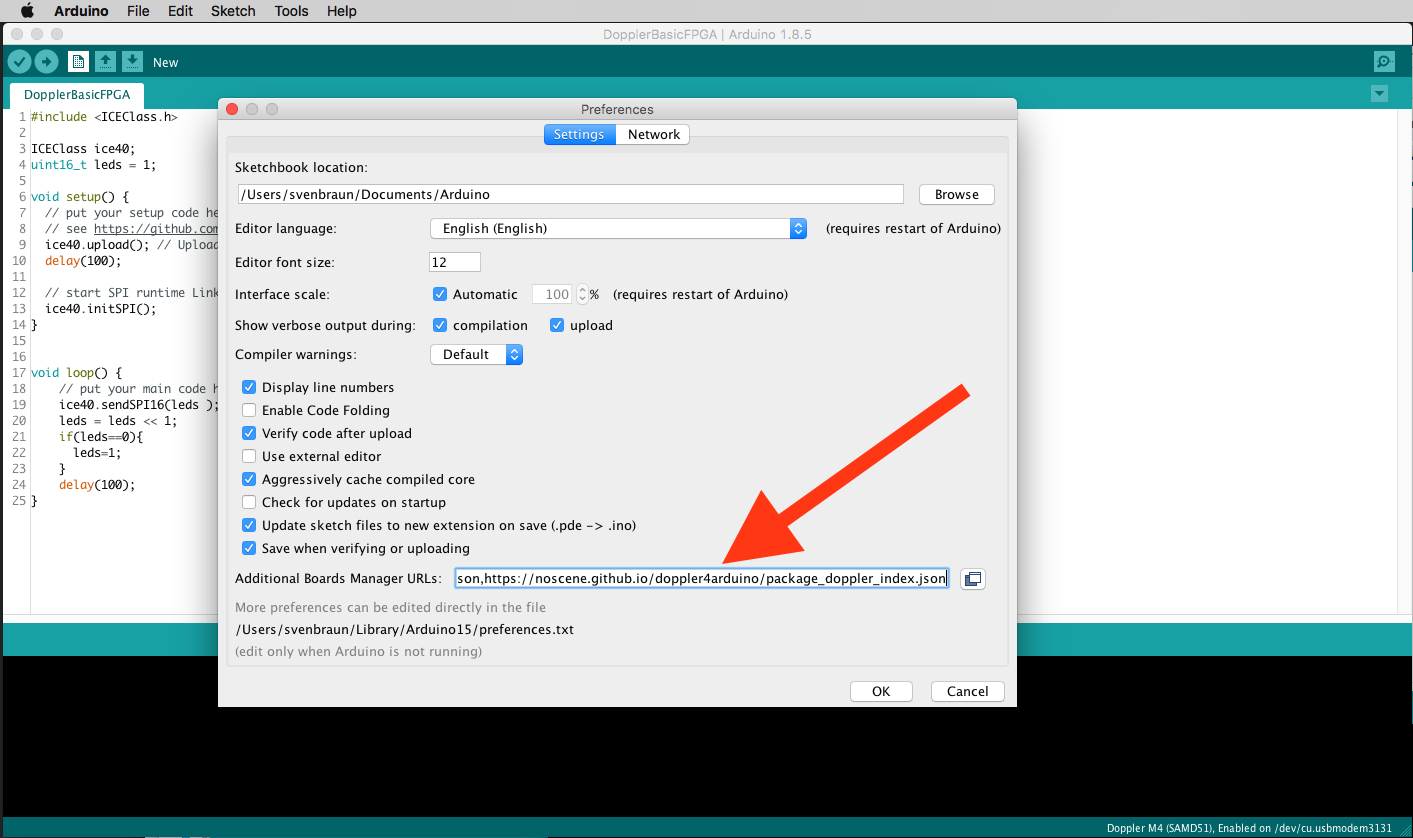 go to boardmanager
go to boardmanager
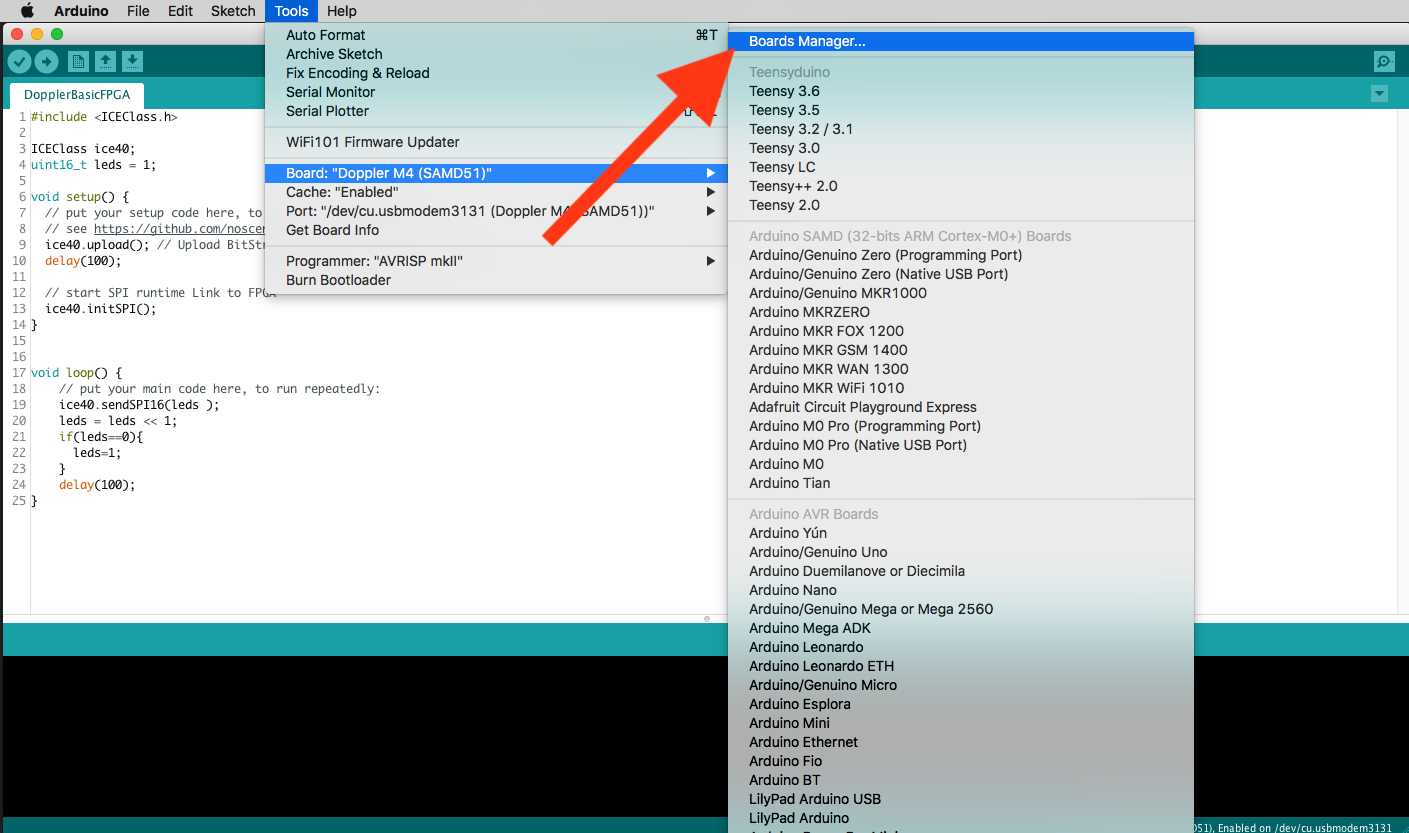 install both boards
install both boards
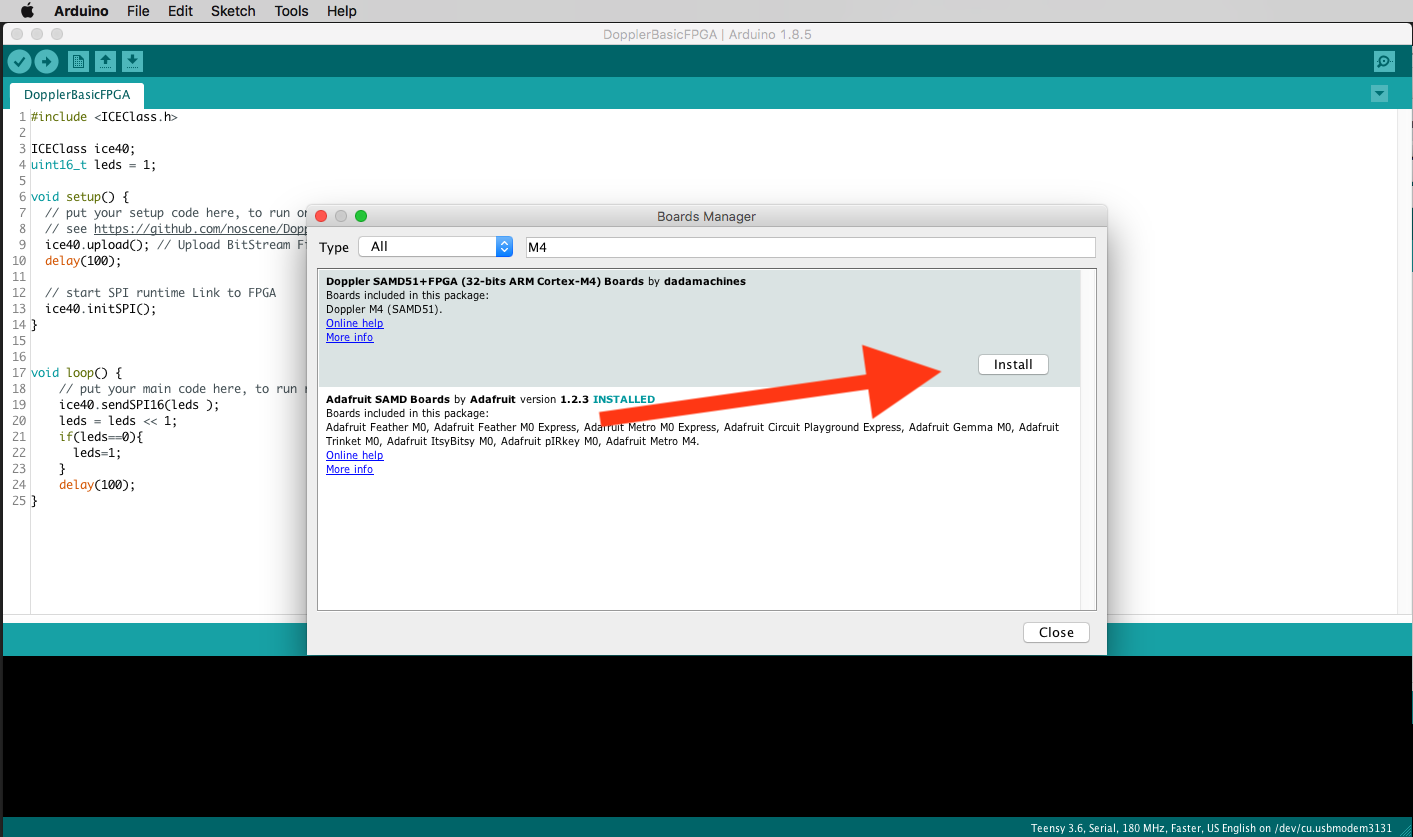 select the Doppler Board
select the Doppler Board
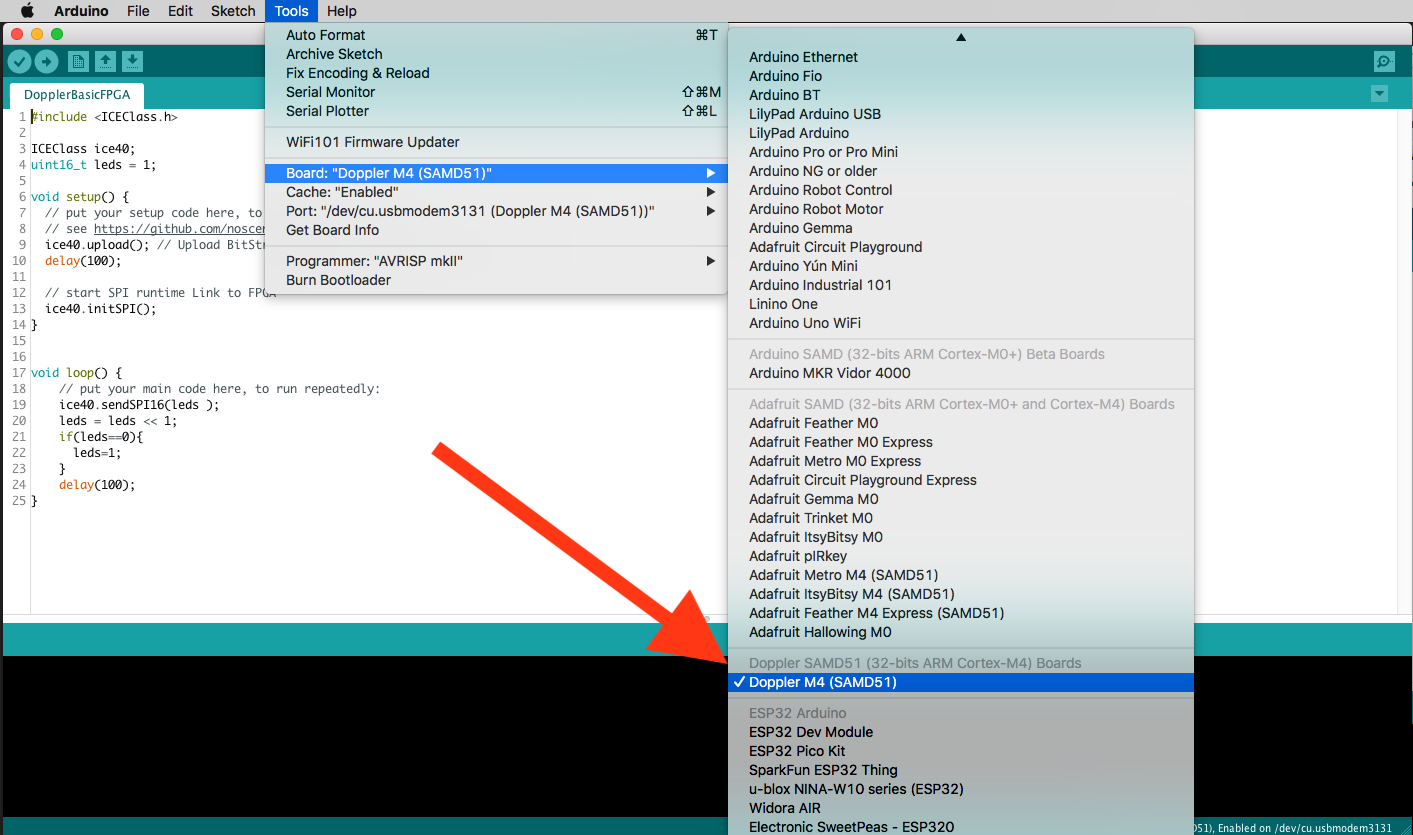 select USB Port
select USB Port
Board Layout and PINs
/* DOPPLER-Board-Layout:
* ---------------- FPGA Pins ------------------
* DAC1 SCK MOSI DAC0 LedR LedG LedB CT1 CP0
* DIL Pin 48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41 40 39 38 37 36 35 34 33 32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25
* |--O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O---|
* name | VIN 5V 3.3V A10 A9 A8 A7 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 GND R2 R1 R0 F14 F13 F12 F11 F10 F9 |
* alt | VIN 5V 3.3V PA11 PA10 PA09 PA08 PA07 PA06 PA05 PA04 PB09 PB08 PA02 GND 41 40 39 38 37 36 35 34 32 |
* | ö ö ö ö |
* | ö ö ö ö |BTN:S1| |
* | USB DOPPLER: SamD51 <- SPI -> icE40 |BTN:RESET| ö ö ö ö |
* | ö ö ö ö |BTN:S2| |
* | |
* alt | GND PA13 PA12 PB11 PA14 PA15 PB10 PA31 PA30 RES PA19 PA20 PA21 PA22 3.3V 11 12 13 18 19 20 21 23 25 |
* name | GND 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 3.3V F0 F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 |
* L--O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O----O---|
* DIL Pin 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
* SCL SDA MISO SS SWD SWC RES CT0 CP0
* -- I2C-- --- SWD --- ----- Shared ----- ---------------- FPGA Pins ------------------
*/
Examples
Blink on board LED
// the setup routine runs once when you press reset:
void setup() {
// initialize the digital pin as an output.
pinMode(LED_BUILTIN, OUTPUT);
}
// the loop routine runs over and over again forever:
void loop() {
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH); // turn the LED on (HIGH is the voltage level)
delay(1000); // wait for a second
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, LOW); // turn the LED off by making the voltage LOW
delay(1000); // wait for a second
}
fast write 2 DAC Channels on A0 and A4 (PA02+PA05)
void setup() {
// put your setup code here, to run once:
pinMode(PIN_DAC0,OUTPUT);
pinMode(PIN_DAC1,OUTPUT);
dacInit();
}
void loop() {
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
static uint16_t left = 0;
static uint16_t right = 0;
left+=256;
right-=256;
dacWrite(left,right);
}
FPGA demo set 4x4 LED Matrix
see https://github.com/noscene/Doppler_FPGA_Firmware for make bitstream from verilog
#include <ICEClass.h>
ICEClass ice40;
uint16_t leds = 1;
void setup() {
// put your setup code here, to run once:
ice40.upload(); // Upload BitStream Firmware to FPGA -> see variant.h
delay(100);
// start SPI runtime Link to FPGA
ice40.initSPI();
}
void loop() {
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
ice40.sendSPI16(leds );
leds = leds << 1;
if(leds==0){
leds=1;
}
delay(100);
}
Show hex chars on 4x4 matrix
#include <ICEClass.h>
ICEClass ice40;
uint16_t hexmapFont[16] = { 0xF99F,0xF22F,0xF42F,0xF17F,0x1F99,0x7F8F,0xF9F8,0x111F,
0x7DBE,0x1F9F,0x9F9F,0xADAC,0xF88F,0xE99E,0xF8EF,0x8E8F };
void setup() { // put your setup code here, to run once:
ice40.upload(); // Upload BitStream Firmware to FPGA -> see variant.h
delay(100);
ice40.initSPI(); // start SPI runtime Link to FPGA
}
void loop() { // put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
for(int i = 0 ; i < 16 ; i++){
ice40.sendSPI16(hexmapFont[i] );
delay(800);
}
}
Create second I2C Bus as Wire1 on pins A7+A8 and scan the bus
see https://learn.adafruit.com/using-atsamd21-sercom-to-add-more-spi-i2c-serial-ports/creating-a-new-wire how to handle sercoms
#include <Wire.h>
#include "wiring_private.h" // pinPeripheral() function
TwoWire Wire1(&sercom0, A7, A8); // create new Wire Port
void setup() {
// put your setup code here, to run once:
Wire1.begin(); // set pinPeripheral after this line!!!
pinPeripheral(A7, PIO_SERCOM); // assign SDA
pinPeripheral(A8, PIO_SERCOM); // assign SDC
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("\nI2C Scanner");
}
void loop() {
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
byte error, address;
int nDevices;
Serial.println("Scanning...");
nDevices = 0;
for(address = 1; address < 127; address++ ) {
// The i2c_scanner uses the return value of
// the Write.endTransmisstion to see if
// a device did acknowledge to the address.
Wire1.beginTransmission(address);
error = Wire1.endTransmission();
Wire1.requestFrom(address,2);
if (error == 0) {
Serial.print("I2C device found at address 0x");
if (address<16)
Serial.print("0");
Serial.print(address,HEX);
Serial.println(" !");
nDevices++;
} else if (error==4) {
Serial.print("Unknow error at address 0x");
if (address<16)
Serial.print("0");
Serial.println(address,HEX);
}
}
if (nDevices == 0)
Serial.println("No I2C devices found\n");
else
Serial.println("done, if find on each addr -> check pullups! \n");
delay(5000); // wait 5 seconds for next scan
}
Create UART RX,TX Serial2 on pins A7+A8
see https://learn.adafruit.com/using-atsamd21-sercom-to-add-more-spi-i2c-serial-ports/creating-a-new-serial how to handle sercoms
// Create Serial2 instance
#include "wiring_private.h" // pinPeripheral() function
Uart Serial2 (&sercom0, A7, A8, SERCOM_RX_PAD_1, UART_TX_PAD_0);
void SERCOM0_0_Handler() { Serial2.IrqHandler(); }
void SERCOM0_1_Handler() { Serial2.IrqHandler(); }
void SERCOM0_2_Handler() { Serial2.IrqHandler(); }
void SERCOM0_3_Handler() { Serial2.IrqHandler(); }
void setup() {
// put your setup code here, to run once:
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial2.begin(9600);
pinPeripheral(A7, PIO_SERCOM); // TX
pinPeripheral(A8, PIO_SERCOM); // RX
}
uint8_t i=0;
void loop() {
Serial.print(i);
Serial2.write(i++);
if (Serial2.available()) {
Serial.print(" -> 0x"); Serial.print(Serial2.read(), HEX);
}
Serial.println();
delay(500);
}
Performance
Classic ArduinoStyle vs direct Register Access
void setup() {
pinMode(0,OUTPUT); // PA13
digitalWrite(0,true);
}
// direct SAMD51 register access PA13
void loop() {
while(1){
PORT->Group[PORTA].OUTCLR.reg = 1ul << 13; // this part generate 30Mhz so it looks like this part need 2 cpu cycles for each pin change
PORT->Group[PORTA].OUTSET.reg = 1ul << 13; // this part generate 30Mhz
}
}
// classic way but not realy fast
void loop_not_very_fast() {
digitalWrite(0,true); // this part generate 0.5 Mhz
digitalWrite(0,false); // this part generate 0.5 Mhz
}